The Power of Positive Reinforcement: Building Confidence and Success
Positive reinforcement is a psychological concept grounded in behaviorism, particularly in the work of B.F. Skinner. It involves encouraging desirable behaviors by providing rewards or positive feedback. The premise is simple: when someone performs a behavior that leads to a positive outcome, they are more likely to repeat that behavior in the future. This strategy is widely used in education, parenting, and even in the workplace to nurture growth, confidence, and improved performance.
But how can this technique be applied to help a struggling student develop self-confidence, especially when they have a history of poor grades? By using positive reinforcement, it’s possible to create a mindset shift that encourages persistence, resilience, and ultimately, success.
How Positive Reinforcement Works
Positive reinforcement is about rewarding behaviors rather than just focusing on the outcomes. When someone receives praise, encouragement, or any kind of reward after making an effort, they begin to associate that action with positive feelings. This strengthens their motivation to repeat the behavior, gradually making it a part of their routine.
For example, in the case of a student who consistently gets poor grades, it’s easy for them to lose confidence and believe they aren’t capable of improving. This can create a downward spiral where the lack of self-belief limits their effort, resulting in continued failure. However, by using positive reinforcement, a teacher or parent can start to change the student’s mindset.
Applying Positive Reinforcement to Boost Confidence
Let’s consider an example of a student struggling with math. Instead of focusing on their past failures or criticizing them for poor performance, the teacher begins to praise every effort they make, even if small. If the student solves a basic problem, the teacher might say, “Great job! You’re really improving,” or “That was a tough question, and you did it—well done!” These words of encouragement build the student’s sense of competence and self-worth.
Even if the progress is slow, the regular use of positive reinforcement ensures that the student starts to associate hard work with positive recognition. Over time, this can help them regain their confidence and push themselves to tackle more difficult challenges. Eventually, the belief that “I am capable of succeeding” replaces the old belief of “I am bad at this.”
Psychological Impact: Building Self-Efficacy
The psychological principle at play here is self-efficacy—the belief in one’s own ability to succeed. By continually reinforcing a student’s effort and highlighting their strengths, positive reinforcement helps to improve their self-efficacy. The student becomes more likely to engage with difficult tasks, persist through failure, and ultimately, improve their academic performance.
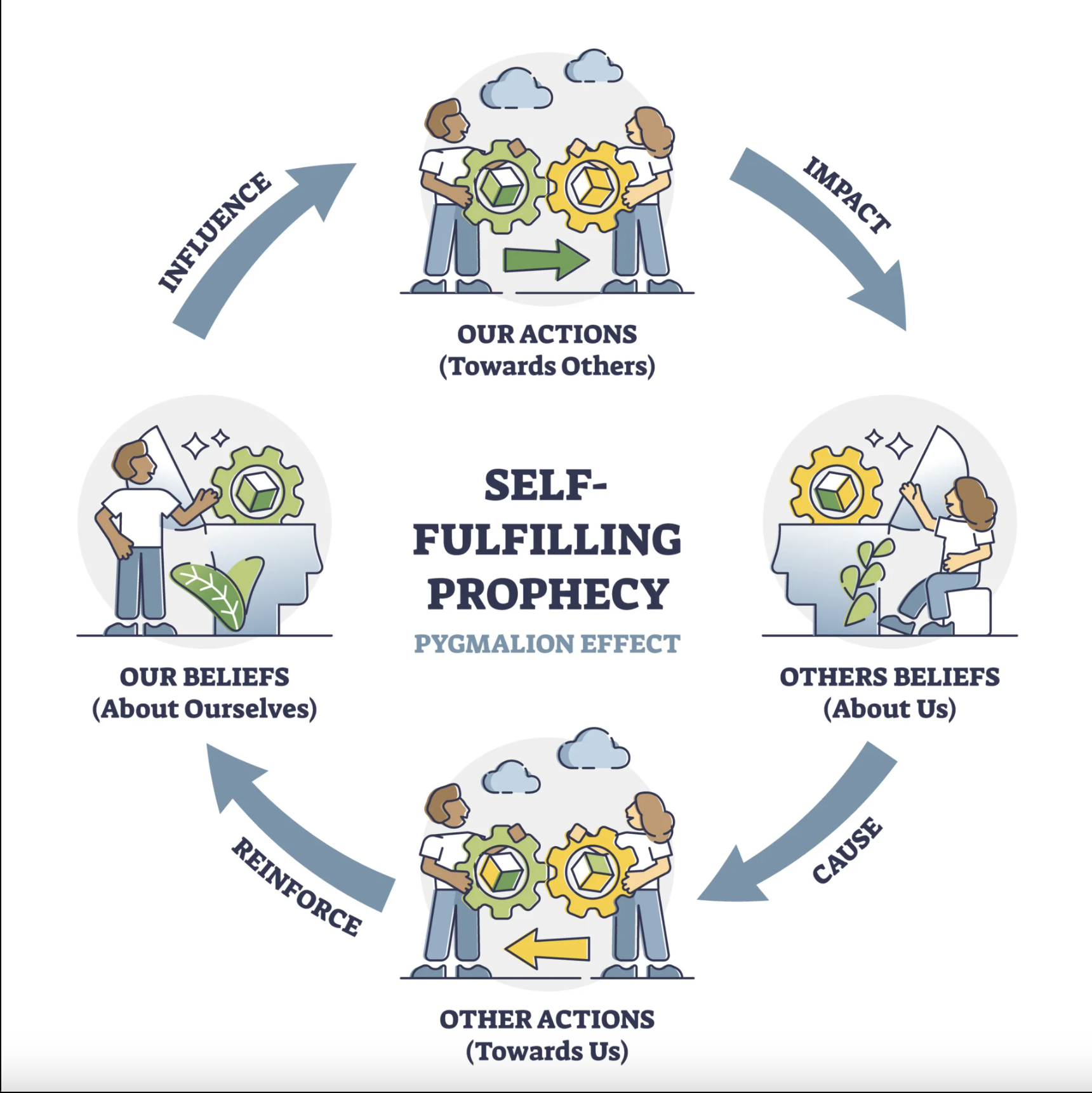
This process can also trigger a self-fulfilling prophecy, also known as the Pygmalion effect. If a student is consistently told they are smart, capable, and strong, they will eventually begin to internalize this message, which can result in them performing at higher levels. The opposite is also true: negative reinforcement or criticism can erode confidence and lead to poorer performance over time.
Practical Examples of Positive Reinforcement in Daily Life
Positive reinforcement isn’t just useful in the classroom; it plays a powerful role in everyday life across a wide range of situations:
- Parenting: A parent might use positive reinforcement by praising their child for completing their homework without being told or for showing kindness to a sibling. “I’m proud of how responsible you’re becoming!” helps solidify the behavior.
- Workplace: Managers can use positive reinforcement by acknowledging employees’ efforts: “Great work on the project—your attention to detail made a real difference!” This feedback can motivate employees to continue excelling.
- Personal Growth: People can apply positive reinforcement to themselves by rewarding their own progress toward personal goals. For instance, after completing a workout, someone might treat themselves to a relaxing evening, reinforcing the habit of exercising regularly.
Harnessing AI for Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is even making its way into technology, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI) systems. AI-driven platforms are increasingly being designed to encourage users’ behaviors through subtle rewards and feedback mechanisms.
For example, AI-powered educational apps can track a student’s progress and provide instant, tailored positive feedback for each small improvement, no matter how minor. If a student answers a question correctly, the app might show encouraging phrases like, “Fantastic! You’re mastering this concept!” With AI’s ability to personalize learning experiences, it can effectively identify which types of positive reinforcement resonate best with individual students, creating a highly customized learning environment.
Another use of AI could be in fitness tracking apps, where the system provides real-time positive feedback based on a user’s progress. If a runner achieves a new personal best, the app could congratulate them with messages like, “New record! Keep it up, you’re unstoppable!” Over time, these small motivational nudges help reinforce the user’s commitment to their goals.
Positive Reinforcement in Social Media
Social media platforms also use positive reinforcement extensively to keep users engaged. Through likes, comments, shares, and other forms of instant feedback, these platforms reinforce users’ posting behavior. Every time a post gets liked or shared, the user receives a small boost of dopamine, which encourages them to keep engaging with the platform.
Social media algorithms are designed to show users content that’s likely to get positive feedback, subtly conditioning them to produce and share more of the same type of content. Features like streaks on Snapchat or reaction emojis on Facebook are examples of how platforms use positive reinforcement to foster habitual use. By rewarding consistent participation or amplifying positive reactions, social media creates a feedback loop that keeps users coming back and spending more time on the platform.
Conclusion
Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool for shaping behavior and building confidence. By focusing on effort and progress rather than perfection, it helps individuals—whether students, employees, or anyone else—believe in their ability to improve and succeed. As technology continues to evolve, AI and social media platforms are increasingly using positive reinforcement techniques to personalize user experiences and encourage engagement, showing just how powerful this psychological tool can be.