Introduction to Boolean Algebra

Introduction to Boolean Algebra: The Foundation of Modern Computing
Boolean algebra, named after the English mathematician George Boole, is a branch of algebra that deals with binary variables and logical operations. Unlike traditional algebra, which works with numerical values, Boolean algebra is concerned with truth values—true and false, often represented as 1 and 0, respectively. This system forms the basis of digital logic used in computer science, electronics, and many other fields.
The Basics of Boolean Algebra
At its core, Boolean algebra involves operations such as AND, OR, and NOT. These operations are used to combine or modify binary variables according to specific rules. For instance:
- AND Operation: Returns true (1) if both operands are true.
- OR Operation: Returns true if at least one of the operands is true.
- NOT Operation: Inverts the value, turning true into false and vice versa.
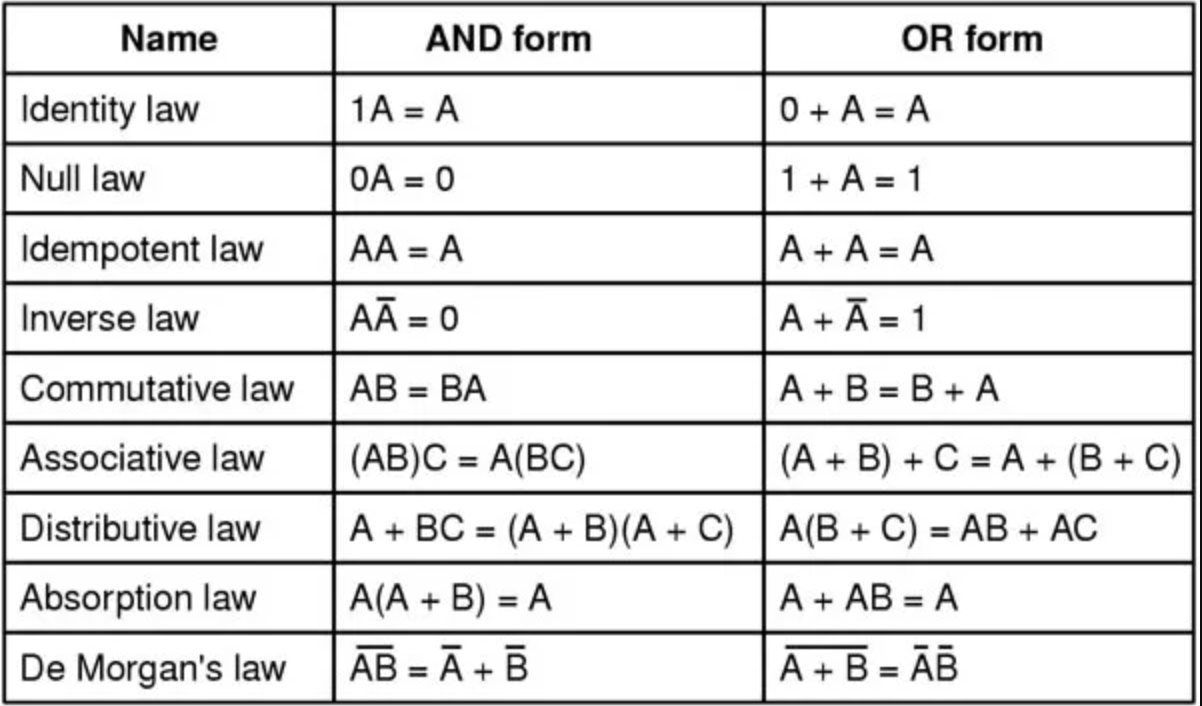
These basic operations can be combined into more complex expressions, which can then be simplified using Boolean identities and laws, such as De Morgan’s laws. This simplification process is crucial in designing efficient digital circuits and logical expressions.
Applications of Boolean Algebra in the Modern World
Boolean algebra is fundamental in the design and operation of digital electronics and computer systems. In electronics, it is used to create and simplify the logic gates that make up the circuits in processors, memory devices, and other components. These logic gates perform basic operations—AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR—that are essential for executing binary instructions in digital devices.
In computer science, Boolean algebra underpins algorithms and data structures that involve decision-making processes. It is also integral to programming, where conditional statements (if-else) rely on Boolean logic to execute code based on specific criteria. Furthermore, Boolean search logic is widely used in search engines and databases to filter and retrieve information based on user queries.
Conclusion
Boolean algebra is more than just a mathematical curiosity; it is the backbone of modern digital technology. From the circuits inside your smartphone to the software algorithms that power the internet, Boolean logic is everywhere, driving the functionality of countless devices and systems. Understanding Boolean algebra not only sheds light on how technology works but also provides the tools to innovate and develop new digital solutions.